We Are The Best Digital Agency For Business
Choose “ITUPDOWN” as your digital marketing agency and
propel your business to new heights with our services
digital marketing materials and our proprietary technology platform.
Our business is to provide strategic digital solutions.
our creation, Since we have developed more than 100 websites
that allow brands to connect with their audience in a way
relevant and meaningful.

All The Great Things We've Done
They're Talking About Us
Core Services
Smart digital marketing includes many sub-services. Our main goal is to choose the most
efficient and get the best result.

LOCAL SEO

WEBSITE DESIGN

WEBSITE DEVELOPMENT
Technical SEO

CONTENT WRITING

WEBSITE AUDIT

Ecommerce Website Development

GOOGLE ADS

SOCIAL MEDIA MARKETING





About Search Engine Optimization
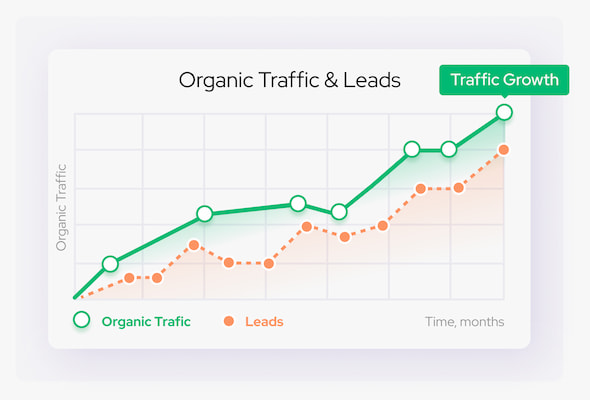
Why Start?
What is SEO?
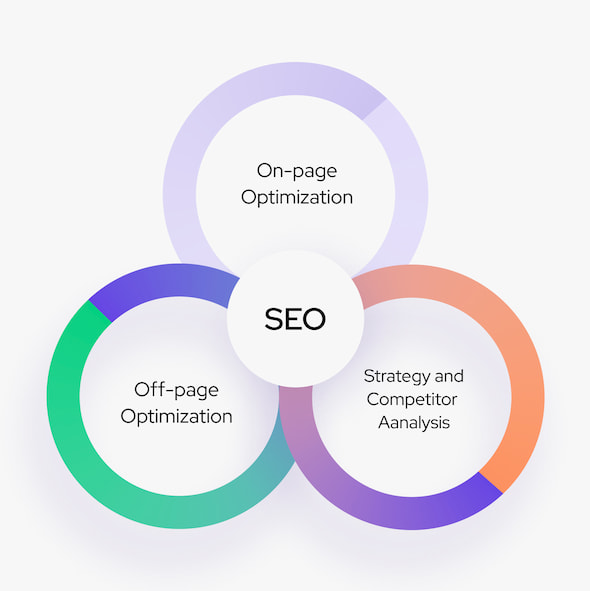
Quality and Robust Online Reseller Services
How Much SEO Services?
amount of keywords, age & quality of the website

Of course, you can hire a specialist and pay him a salary of about 500 – 100$ to do the entire project, but he will never be able to physically & mentally provide you the same amount of works as an SEO company.
Why Our SEO Company?
Our website holds the top-3 position for all popular keywords in the niche.

More than 50+ websites on the 1st-page of organic search results

Half Payment in Advance

100% Guarantee

Online Reporting 24/7

Eleven Years of Experience

Dedicated Account Manager
Our Team
Samy- Digital Marketing
Muhammad - Developer
Experienced software developer with 3+ years of experience in the industry. Proven ability to design, develop, and deliver high-quality software solutions.
